- خانه
- خدمات
- دیالیز
- فروشگاه
- آموزش
- کتاب ها
- آموزش پرستاری
- آموزش همودیالیز
- آموزش تئوری
- آناتومی و فیزیولوژی
- نارسایی حاد کلیه
- نارسایی مزمن کلیه
- همودیالیز
- انواع دیالیز
- مکانیسم دیالیز
- وزن خشک
- تصفیه آب
- پروتکل درمانی همودیالیز در بیماران حاد
- دسترسی عروقی
- اختلالات کلسیم، فسفر و اوستئودیستروفی در بیماران دیالیزی
- آنمی در بیماران مبتلا به نارسایی مزمن کلیه
- آنتی کواگولاسیون در همودیالیز
- محلول همودیالیز
- انواع و خصوصیات صافی ها
- کفایت دیالیز
- عوارض دیالیز
- مراقبت های حین دیالیز
- کنترل عفونت بیمارستانی در بخش همودیالیز
- بیماری های ویروسی
- دارو و دیالیز
- تغذیه
- تجهیزات مصرفی
- آموزش عملی
- کاتالوگ
- آموزش تئوری
- آموزش دیالیز صفاقی
- آموزشCRRT
- آموزش دیالیز SLED
- آموزش هموپرفیوژن
- اموزش پلاسمافرزیس
- آموزش همودیالیز
- آموزش به بیمار
- نمونه سوالات پایان همودیالیز
- آزمون پایانی همودیالیز
- ازمون همودیالیز ۱
- آزمون پایانی همودیالیز ۲
- مدرسه کلیه
- مجله دیالیز
- درباره ما
- KTV
- خانه
- خدمات
- دیالیز
- فروشگاه
- آموزش
- کتاب ها
- آموزش پرستاری
- آموزش همودیالیز
- آموزش تئوری
- آناتومی و فیزیولوژی
- نارسایی حاد کلیه
- نارسایی مزمن کلیه
- همودیالیز
- انواع دیالیز
- مکانیسم دیالیز
- وزن خشک
- تصفیه آب
- پروتکل درمانی همودیالیز در بیماران حاد
- دسترسی عروقی
- اختلالات کلسیم، فسفر و اوستئودیستروفی در بیماران دیالیزی
- آنمی در بیماران مبتلا به نارسایی مزمن کلیه
- آنتی کواگولاسیون در همودیالیز
- محلول همودیالیز
- انواع و خصوصیات صافی ها
- کفایت دیالیز
- عوارض دیالیز
- مراقبت های حین دیالیز
- کنترل عفونت بیمارستانی در بخش همودیالیز
- بیماری های ویروسی
- دارو و دیالیز
- تغذیه
- تجهیزات مصرفی
- آموزش عملی
- کاتالوگ
- آموزش تئوری
- آموزش دیالیز صفاقی
- آموزشCRRT
- آموزش دیالیز SLED
- آموزش هموپرفیوژن
- اموزش پلاسمافرزیس
- آموزش همودیالیز
- آموزش به بیمار
- نمونه سوالات پایان همودیالیز
- آزمون پایانی همودیالیز
- ازمون همودیالیز ۱
- آزمون پایانی همودیالیز ۲
- مدرسه کلیه
- مجله دیالیز
- درباره ما
- KTV
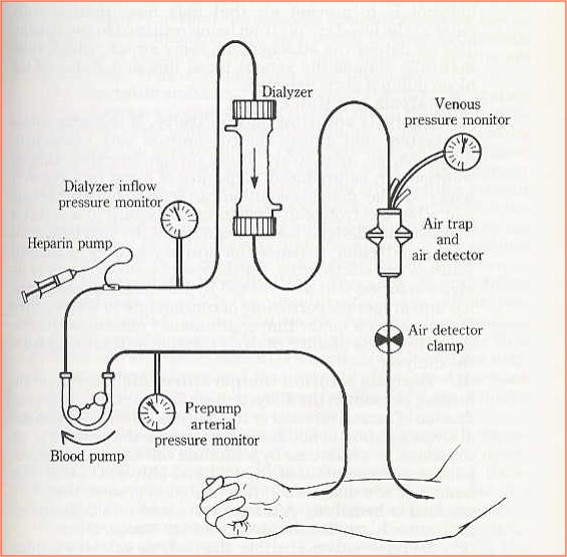
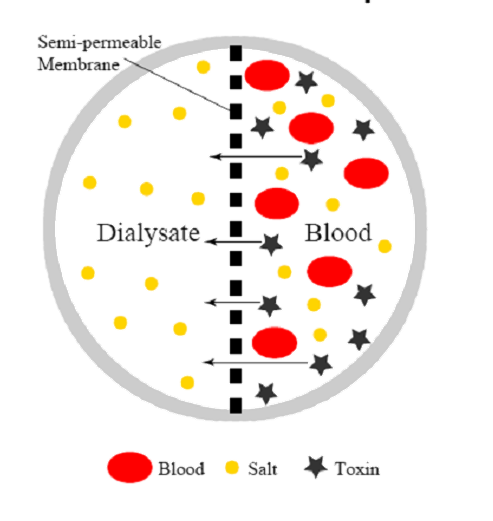
The principle of Dialysis
The principle of Dialysis
principle of haemodialysis
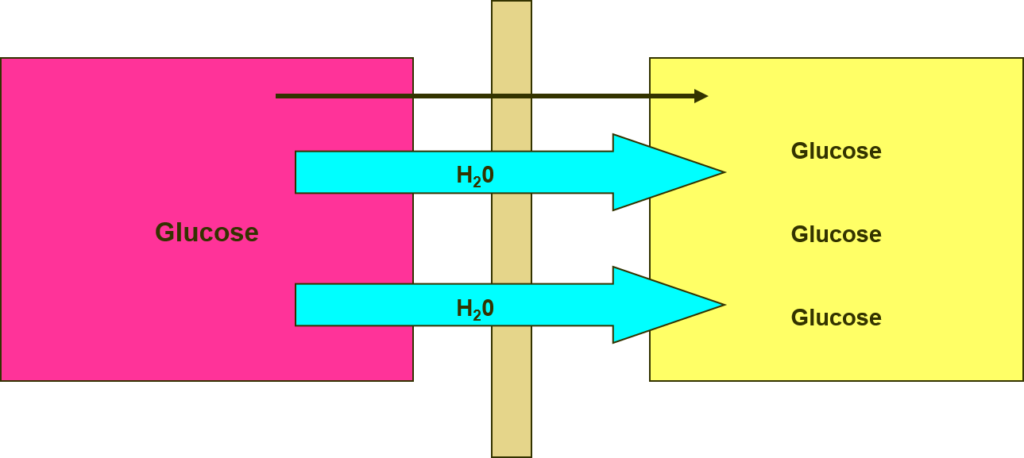
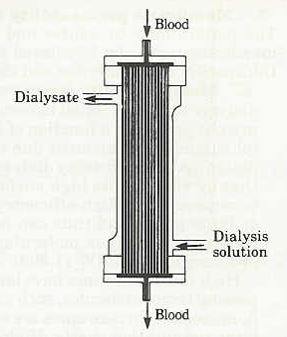
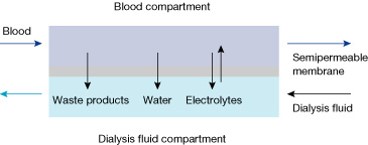
- Blood flows on one side of a semipermeable membrane, and dialysis fluid, an osmotically balanced solution of electrolytes, buffer, and glucose in water, flows on the other.
- The pores of the semipermeable membrane allow water molecules and small molecular weight solutes to pass through into the dialysate, but larger solutes such as proteins and blood cells are retained in the blood.
Solute transport
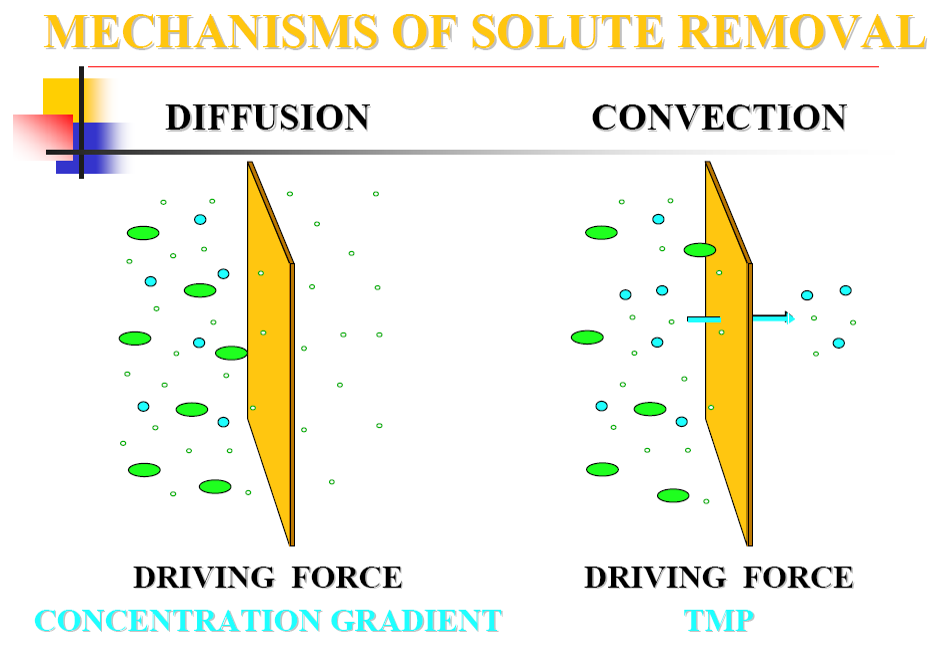
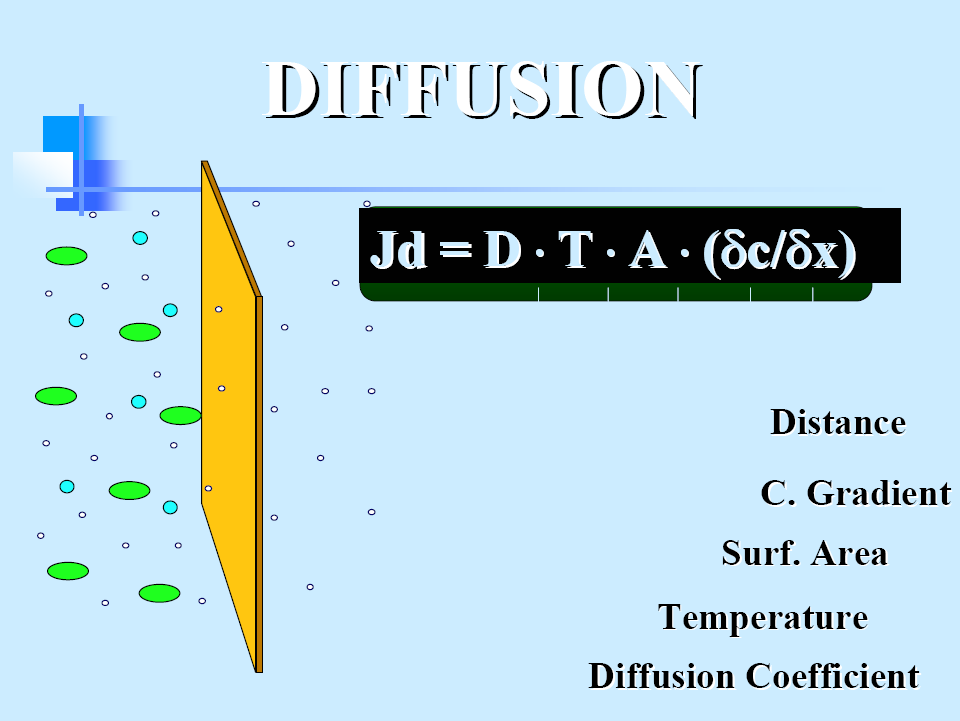
Diffusion
ultrafiltration-based convection
The net rate of passage of a given solute across the membrane depends on the magnitude and direction of its concentration gradient between blood and dialysate.
To maintain a maximal concentration gradient during haemodialysis, blood and dialysis fluid flow through the compartments in opposite directions
:Solute Clearance Depends upon
- Concentration gradient
- Blood flow rate
- Dialysate flow rate
- Properties of dialysis membrane
- Size and physicochemical properties of solutes
Small solute clearance depends on blood flow rate
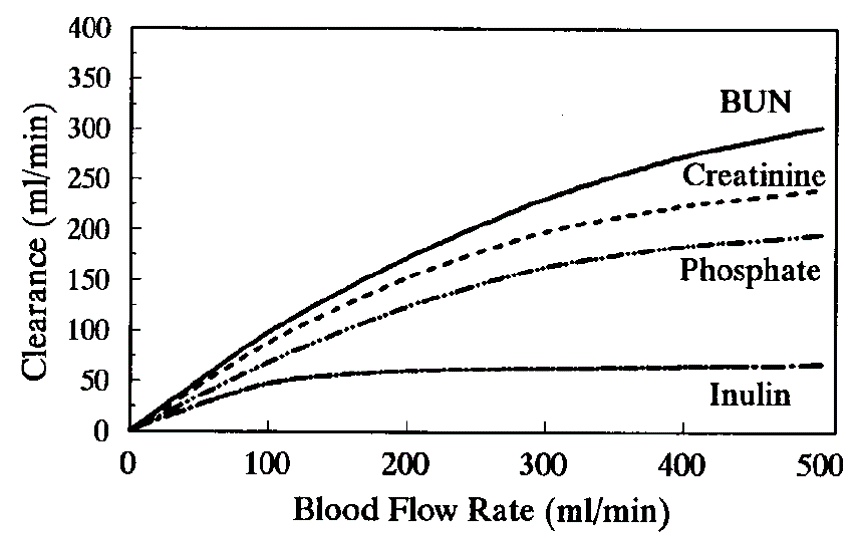
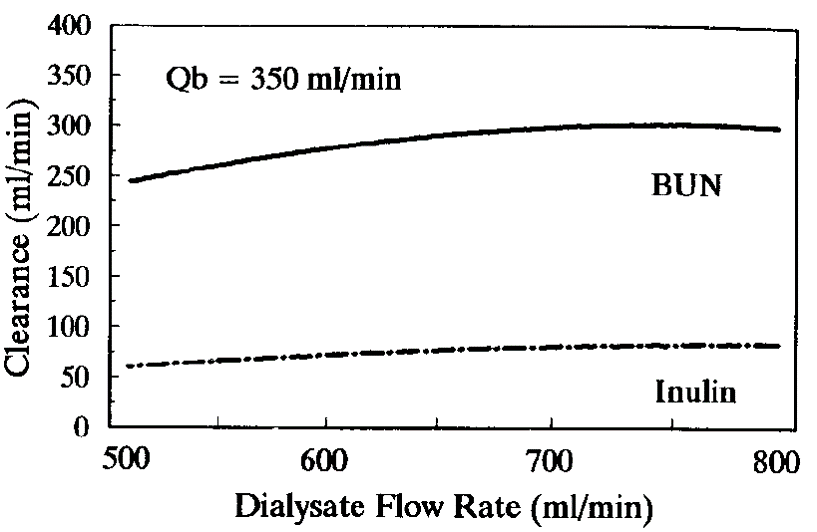
The rate of diffusion
molecular weight
the membrane resistance to diffusion, decreasing with increasing molecular weight and increasing membrane resistance.
The resistance of the membrane
high if the membrane is thick and if there are few pores which are small in size.
Additional factors
size, shape, and charge of the molecules.
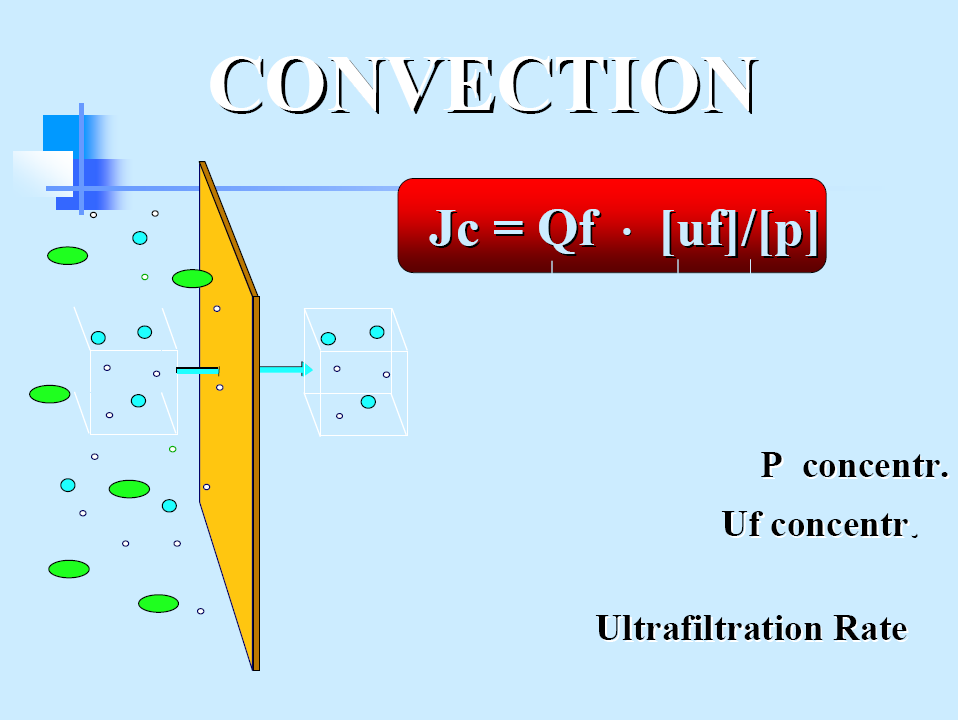
Ultrafiltration
- remove excess water from the patient. If, for instance, the hydrostatic pressure is greater in the blood compartment than in the dialysate compartment, the small water molecules are forced through the membrane from blood to dialysate. In a process called solvent drag,
- solutes with low molecular weights that can pass through the membrane pores are swept along with the water
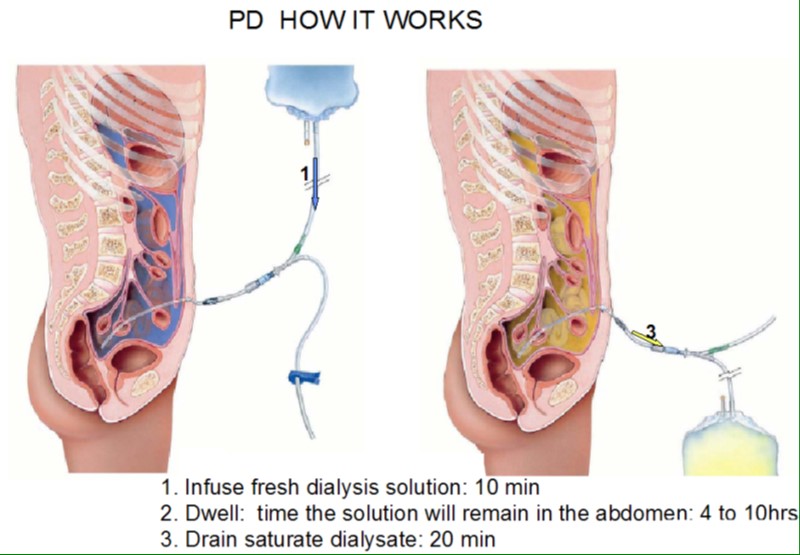
Peritoneal Dialysis
: The transport of solutes and water across a membrane that separates 2 fluid containing compartments
- Blood in the peritoneal capillaries
- Dialysis solution in the peritoneal cavity
PD : How It Works
Transport processes
-
Diffusion
-
Convection
-
Absorption
The three - pore model
-
Large pores ( 20 – ۴۰ nm )
- Transport of macromolecules
- Vary in size
-
Small pores ( 4.0 – ۶.۰ nm )
- Transport of small solutes
- Constant radius
-
Ultra small pores ( <0.8 nm)
- Transport of water
Peritoneal diffusion (1 )
- Concentration gradient
- Maximal at the start
- More frequent exchange
- Increasing dwell volume
Peritoneal diffusion (2 )
- Effective peritoneal surface area
- Total surface area
- Degree of vascularity
- Larger fill volumes
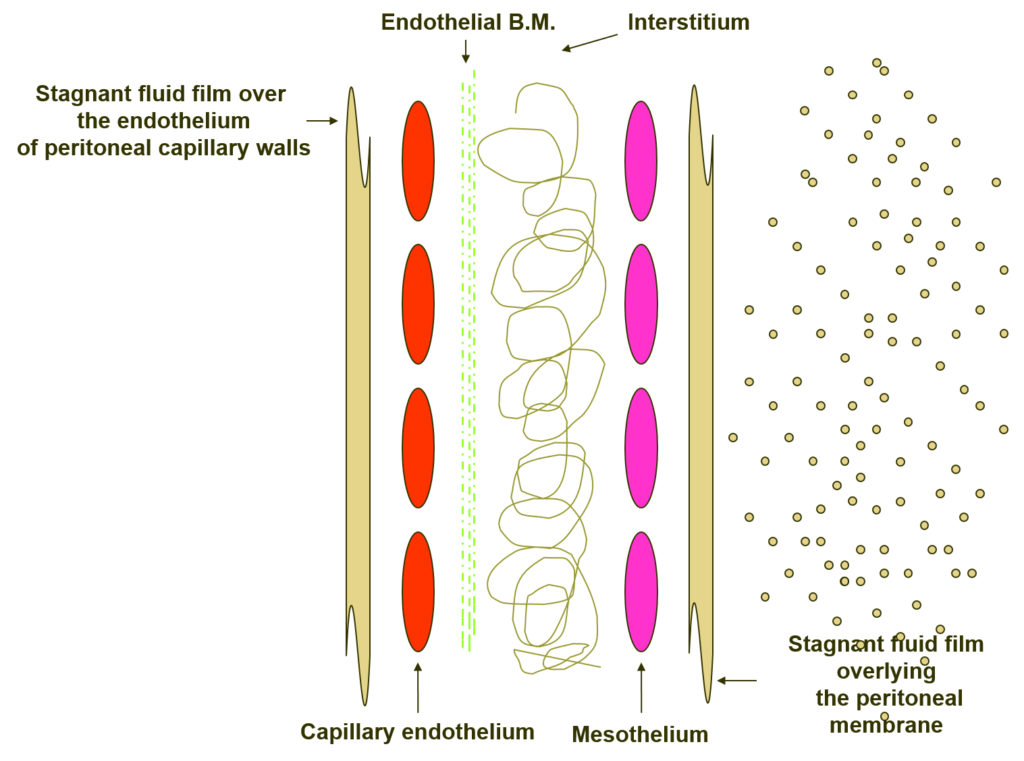
Peritoneal diffusion (3 )
- Intrinsic membrane resistance
- Difference in the number of pores
- Distance of capillaries and mesothelium
- Molecular weight of the solute
- Low versus high
Peritoneal convection
- Solute transport with ultrafiltration
- Water transport induced by osmotic gradients
PD : How It Works
PD : How It Works